
Inserting or removing a circuit board from a live backplane can cause damaging transients unless appropriate design considerations are taken.
ITraditional solutions have used an integrated circuit (IC) with an external MOSFET. With board space at a premium, especially in telecom, networking or any application where the board dimensions are fixed, a more integrated solution is a must have. Negative voltage hot swap (NVHS) controllers that integrate the switch MOSFET, not only save the space of the large switch, but also reduce the number of external components such as sense resistors. The NVHS IC protects the board from transients that can occur during hot-swapping and reduces the board space required for this power management function freeing-up space for adding additional functions that differentiate the board.
What happens without hot-swap protection
When a circuit board is inserted into or removed from a live backplane, the filter or bypass capacitors that are being charged or discharged at the input of the board's power module or switching power supply can cause large transient currents. These currents can cause severe and permanent damage to the board making the system unstable. In addition, the repairs can cause costly warranty problems and downtime. The waveform with the transient that can occur in an unprotected system is shown in Figure 1a.
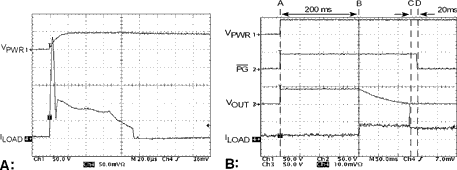
What happens with hot-swap protection
With a hot-swap IC, when the board is inserted into the live backplane, inrush current is limited and the power is ramped to the load in a managed way. This shields the bypass capacitors from sudden application of power, hence preventing fast and uncontrollable transients. Figure 1b shows how well the power is managed and inrush current is controlled using a hot-swap.
Space considerations
With the goal of saving board space as one of the primary considerations, selecting the right package is one of the most important silicon design decisions. If the complete circuitry could fit in something as small as an 8-pin SOIC (a high volume, cost-effective package with established reliability) then the solution will satisfy key requirements in integration and cost. The eight pins would also allow additional functions to be provided. The case outline of the SOIC-8 package is a maximum 5 x 6,2 mm (31 mm²). By not having to add an external FET in either a SOT-223 (6,7 x 7,29 mm = 48,8 mm²) or a DPAK (6,73 x 10,42 mm = 70,1 mm²), a minimum of about 61% (neglecting the interconnections) and as much as 69% space could be saved for this function since the DPAK is over twice the size of the SOIC-8.
A top-of-the-line mixed-signal silicon process can be used to integrate the digital logic and precision analog circuitry with a highly efficient, low RDS(ON) power MOSFET. This allows for integration of circuitry that not only provides the hot-swap function but also other very important and key features for a hot-swap controller to perform its function optimally. Some of these features include programmable over-current limit, programmable charging current limit, start-up and retry delay timer, over-voltage and under-voltage detection, active high and/or low power good output signals, a disable input with active-low or active-high capability, and thermal shutdown. The efficient mixed signal process allows for all of this to be included in an SOIC-8 package.
An integrated hot-swap solution
With the hot-swap function being a customer expectation in many applications, the designer's role in implementing this function should be minimal, so he/she can focus on design aspects that differentiate their product. However, the potential damage from a hot-swap event can cause significant customer dissatisfaction so the designer must provide a robust design for this function. An integrated solution in a proven, high volume package solves this dilemma.
For those applications that require programmability for over/under-voltage and start-up timer or up to 2,25 A current-limiting capability, Freescale's MC34652 provides a most versatile solution. Selecting the appropriate resistor values allows the designer to customise the over/under-voltage, the setting of the delay timer, the value and rise time of the charging current, ICHG and the value of the overcurrent limit to satisfy the needs of a fully integrated hot-swap system.
These additional functions require a 16-pin SOIC. However, if the application requirements are very straightforward, Freescale's MC34653 provides the NVHS function in an SOIC 8-pin package.
| Tel: | +27 11 236 1900 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.ebv.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about EBV Electrolink |
| Tel: | +27 11 923 9600 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.altronarrow.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Altron Arrow |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved