
Ultra-Wideband’s (UWB) precision and accuracy are what sets it apart from other location services. With many large corporations leading the charge into research in this field, the technology is growing at a rapid pace. But what exactly is UWB technology? In the early 2000s, global positioning systems (GPS) found their way into mainstream use. The convenience of GPS technology was a huge advance in location technology, giving way to a new level of convenience. For businesses, the benefits go way beyond convenience, with many business models built directly on GPS technology.
Another breakthrough took place ten years later when navigation moved indoors with the application of sensors and communication technologies. These technologies (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee and Thread) allowed devices to be located in indoor environments. This allowed the position of objects to be determined (and by extension, the location of people carrying those objects), which introduced a plethora of new applications.
Why do we need UWB?
However, using only Wi-Fi or BLE, position accuracy can only reach several metres, which is not suitable for precise location tracking. Secondly, when hundreds or thousands of location devices are deployed, real-time location services (RTLS) cannot be efficiently dealt with due to collisions and interference on the communication system.
UWB is a metamorphosis of the traditional location-based systems everyone already knows and uses. This technology offers highly accurate, precise, and valuable location information across varied platforms and applications.
For UWB to be successful it needs to exhibit certain traits:
• The location needs to be precise with a high degree of accuracy.
• The technology must be secure – the location must be kept private to all except the certified communicating devices.
• The location needs to be reliable and consistent, even in harsh and noisy environments.
• The technology needs to be easily scalable.
• Latency in readings needs to be low so that movement of devices can be tracked in real time.
• Location devices need to be small, low-powered, and affordable so that they may be embedded in any device.
Even though UWB was developed in the early 2000s, the technology was used only in military applications like short-range imaging and covert communications, and in medical imaging.
UWB technology is based on the IEEE standard 802.15.4a/z, which has been optimised for micro-location and secure communication. It can locate devices to within a few centimetres, making it 100 times more accurate than the current implementations of Wi-Fi and BLE.
UWB is ideal for RTLS, for the following reasons:
• Because of its high immunity to interference, UWB is reliable.
• With update rates of up to 1000 times, UWB offers very low latency.
• CMOS technology makes UWB both affordable, and optimised for low power.
• UWB uses distance-bounding techniques defined by the IEEE to provide a level of security that makes it extremely secure.
Another reason for the surge in UWB technology is that major smartphone manufacturers like Samsung, Apple and Huawei are involved in projects including chip and antenna design and production. Samsung, together with Xiaomi, NXP, Bosch and other large players are part of the FiRa
How does UWB work?
UWB is a pulse radio technology used in the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. A UWB transmitter works by sending out up to one billion pulses per second
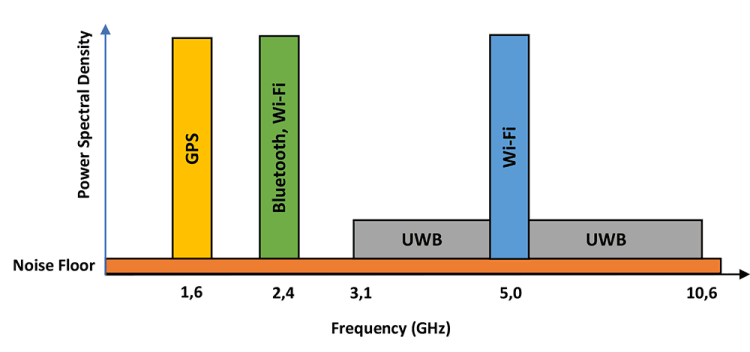
Covering a range of high frequencies from 3,1 to 10,6 GHz, UWB is a line-of-sight system. Penetration through obstacles is extremely poor at this frequency, making the technology area-bound, thereby increasing the security.
The spectral density is also restricted to -41,3 dBm/MHz, which, coupled with pulse-based transmission, minimises the interference with other technologies operating in the same frequency band.
There are four types of antenna systems used for UWB:
• Microstrip antennas are low-profile, low-cost antennas which are easy to fabricate.
• Flexible wearable antennas are used in WBAN
• Wideband monopole antennas provide efficiency.
• Distributed antenna layouts utilising a MIMO system have been added to the standard that enables short-range networks, and this antenna system can be easily embedded into UWB devices. The distributed antennas increase transmission range and data rates.
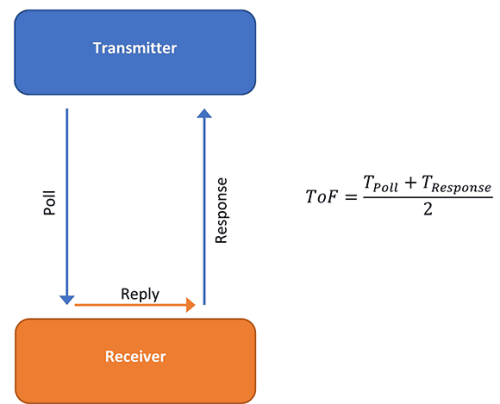
When two UWB devices come into proximity to each other, they start ranging. This ranging is accomplished using the ‘time of flight’ method. The total communication round trip time is measured
On top of the calculated distance, UWB also uses the received signal strength indicator (RSSI) and the Angle-of-Arrival (AoA) simultaneously, to determine the precise location of the receiver.
Besides the ToF, another method of determining the receiver location is Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA). This method requires two anchor devices to be installed in precise, fixed locations. These devices are synchronised and provide accurate position data. The signals coming from the anchors and other UWB devices are time stamped and collated to determine the difference in arrival times. In this way, the UWB device’s location can be precisely pinpointed.
According to the FiRa Consortium, UWB can determine the relative position of peer devices with line-of-sight up to 200 m. This technology allows for smart actions, using UWB devices. For example, carrying a UWB smartwatch connected to an intelligent door could unlock the door on approach, but then lock the same door when the smartwatch moves away. Intelligent lighting could also be implemented in a similar way.
The technology could also enable increased security. A user could be granted access to a bank’s ATM only if a specific UWB device is present. This could also prevent ‘man-in-the-middle’ attacks as a UWB device can be programmed to ignore all other devices present in an area.
Now that major players such as those companies involved in the FiRa Consortium have started implementing the technology into their smartphones and other devices, the technology is set to take off, with more and more applications for the technology being developed.
| Tel: | +27 11 543 5800 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.technews.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Technews Publishing |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved