
South Africa
• Defence and technology company, Denel, is now ranked among the top 100 global defence manufacturers, and the second largest in the southern hemisphere, according to analysis by the international publication, Defense News, and based on revenue achieved during the 2014 financial year. This is the first time that Denel has entered the global top 100 list in the company’s history. Group chief executive, Riaz Saloojee, says the ranking reflects the rapid growth in the company’s revenue over the past four years, from R3,2 billion in 2011 to R4,6 billion in 2014. Since the publication of the report Denel announced a further 28% increase in revenue for the 2014/15 financial year.
Overseas
Business
• For Cypress Semiconductor’s second quarter of 2015, the first full quarter since its buyout of Spansion, the company recorded revenues of $484,8 million and a net loss of $90,1 million ($0,27 per diluted share). The merger process has seen Cypress shed more than 800 staff members and close 19 sites to date, with yet more planned. The company says these cost-cutting measures achieved $51,6 million in annualised synergies in the second quarter, ahead of its plan to achieve $160 million in synergies.
• Analog Devices achieved record revenues of $863 million for its third fiscal quarter – an increase of 19% over last year and 5% more than the second quarter. Net income was $216,5 million (diluted earnings per share (EPS) of $0,68), compared to net income of $205,3 million (diluted EPS of $0,65) in the third quarter of 2014, and net income of $180,6 million (diluted EPS of $0,57) in the second quarter of 2014.
• With NXP Semiconductors’ acquisition of Freescale Semiconductor currently on track to close by year-end, Freescale’s second quarter results impressed with record gross margin (48,1%) and adjusted EPS ($0,57). Net sales for the second quarter of 2015 were $1,20 billion, compared to $1,17 billion in the first quarter of 2015 and $1,19 billion in the second quarter of 2014.
• ams reported second quarter 2015 results at the high end of expectations with year-on-year and quarter-on-quarter growth in revenues and earnings. This propelled the company to revenues for the first half of 2015 of 322,9 million Euros, up 68% over the first half of 2014. Diluted EPS was 0,58 Euros, compared to 0,31 Euros for the second quarter of 2014.
Companies
• RS Components has signed a global distribution agreement with Chauvin Arnoux, a specialist in electrical test and measurement equipment, which extends the scope of the partnership to all markets in the Asia-Pacific and the Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) regions. Products stocked by RS Components include portable handheld multimeters, testers, analysers and oscilloscopes; as well as energy meters, power monitors and digital transducers to measure, test, record, count and monitor MV/LV electric networks in switchboard operation, industrial installation or utilities, for example.
• ams has acquired the CMOS Sensor Business from NXP Semiconductors, expanding its environmental sensor portfolio with advanced monolithic and integrated CMOS sensors that measure several environmental variables such as relative humidity, pressure and temperature in one sensor device. ams anticipates this will drive high-value growth opportunities for smartphones, wearables and other mobile devices, as well as for smart buildings and the industrial, medical and automotive markets.
• Rohm Semiconductor has completed its acquisition of Powervation, a privately held digital power IC company that develops digital power management system-on-chip (SoC) solutions. The all-cash transaction is valued at approximately $70 million. Powervation’s proprietary DSP control platform with patented auto-tuning and intelligent transient management technologies, has been adopted by industry leading customers who need advanced power management, precision telemetry/control and high-efficiency solutions to power their complex multi-rail, multi-phase systems.
Industry
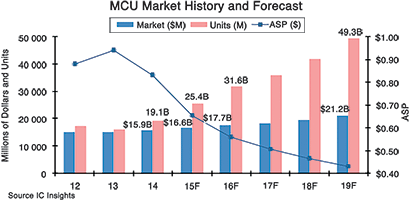
• Microcontrollers (MCU) are in the middle of an incredible wave of unit growth, but unprecedented price erosion is keeping a lid on the increase of revenues, according to IC Insights. The mid-year forecast shows MCU shipments rising 33% in 2015 to 25,4 billion worldwide as a result of a tremendous upsurge in units for smartcards and 32-bit applications, many of which are aimed at the Internet of Things (IoT) market. However, as shown in the graph below, average selling prices are expected to plunge by 21% in 2015 to $0,65.
• The Weightless Special Interest Group (SIG) has created a working group for the development of a new high-performance LPWAN standard – Weightless-P – which will boast features not currently addressed by operator services. It will support all major licence-exempt SRD/ISM bands including 169, 433, 470 – 510, 780, 868, 915 and 923 MHz, and provide fully acknowledged two-way communication at data rates ranging from 200 bps to 100 Kbps.
Using common, commercially available chipsets it will also support both stationary and mobile end devices by utilising low-power, innovative handover, cell re-selection and roaming methods.
Technology
• Researchers have created a new ‘plasmonic oxide material’ that could make possible devices for optical communications that are at least 10 times faster than conventional technologies. Researchers at Purdue University have shown how an optical material made of aluminium-doped zinc oxide (AZO) is able to modulate how much light is reflected by 40% while requiring less power than other all-optical semiconductor devices. They found that the material’s cycle time for light to be absorbed, excite electrons, produce holes and then recombine, was about 350 femtoseconds, which is roughly 5000 times faster than crystalline silicon and so fleeting that light travels only about 100 microns, or roughly the thickness of a sheet of paper, in that time.
• A team of scientists from Columbia University, Seoul National University (SNU) and Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) have demonstrated, for the first time, an on-chip visible light source using graphene, an atomically thin and perfectly crystalline form of carbon, as a filament. They attached small strips of graphene to metal electrodes, suspended the strips above the substrate, and passed a current through the filaments to cause them to heat up. Creating light in small structures on the surface of a chip is crucial for developing fully integrated photonic circuits that do with light what is now done with electric currents in semiconductor integrated circuits.
© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved