
A French vineyard in the Loire valley is a beautiful sight, but the farm has trouble recruiting workers to weed their organically grown grapes. The young generation has moved to the cities leaving urban communities short on workforce. Solution: a fully autonomous tractor, developed by a French-based company Sitia, working tirelessly to weed the narrow rows between the grape vines.
After a full month of weeding and hundreds of kilometres covered, Sitia approached the farmer to review the work done, and reimburse 2 grape vines, which were damaged during the month of operation. They were surprised to hear the farmer exclaim, “When I use my manual tractor to get the same job done, I damaged at least two vines a day! How did your robot manage to be so careful?”.
A high level of accuracy and integrity ensures high quality of autonomous operation. But what exactly is integrity of positioning and how does it affect the performance and reliability of robots and other autonomous machines? Integrity is the truthfulness of positioning and positioning accuracy information, even if it means showing that the current position information is not as accurate as desired in a certain challenging environment. A part of delivering high-integrity positioning is a statistical analysis called RAIM or RAIM+, where the latter takes this analysis to the next level as part of a larger positioning protection package.
Why is integrity critical for automation?
Let us take a closer look at GNSS receiver integrity in the sense of truthful reporting of possible positioning inaccuracies, and how overly optimistic reporting can result in hazardous autonomous operation. Reporting of receiver accuracy is done through positioning uncertainty, which is the maximum possible error on the calculated position. It gives a sense of risk of a positioning error especially necessary in challenging GNSS environments where the receiver “sees” only a limited number of GNSS satellites or where GNSS signals are degraded. Such error reporting is important for all autonomous machines, but especially for assured PNT applications and mission critical operations. Keep in mind that a consistent position may look accurate but could still be incorrect. The positioning uncertainty gives an indication to which extent you can rely on the positioning accuracy at any given moment.
RAIM vs RAIM+
The underlying mechanism behind truthful positioning uncertainty reporting is RAIM (Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring), which ensures truthful positioning calculation based on statistical analysis and exclusion of any outlier satellites or signals. Septentrio receivers are designed for high integrity and take RAIM to the next level with RAIM+, guaranteeing truthfulness of positioning with a high degree of confidence. In Septentrio receivers RAIM+ is actually a component of a comprehensive receiver protection suite called GNSS+ comprising positioning protection on various levels including AIM+ anti-jamming and anti-spoofing, IONO+ resilience to ionospheric scintillations and APME+ multipath mitigation.
The Septentrio RAIM+ statistical model has been fine-tuned with over 50 terabytes of field data collected over 20 years. It removes satellites and signals which may give errors due to multipath reflection, solar ionospheric activity, jamming and spoofing, while working together with the GNSS+ components mentioned above. Because of this multi-component protection architecture, it achieves a very high level of positioning accuracy and reliability which goes well beyond the standard RAIM. The RAIM+ statistical model is adaptive, highly detailed and complete, taking advantage of all available GNSS constellations and signals. The full RAIM+ functionality is even available in Septentrio’s GNSS/INS receiver line. User controlled parameters allow it to be tuned to specific requirements.
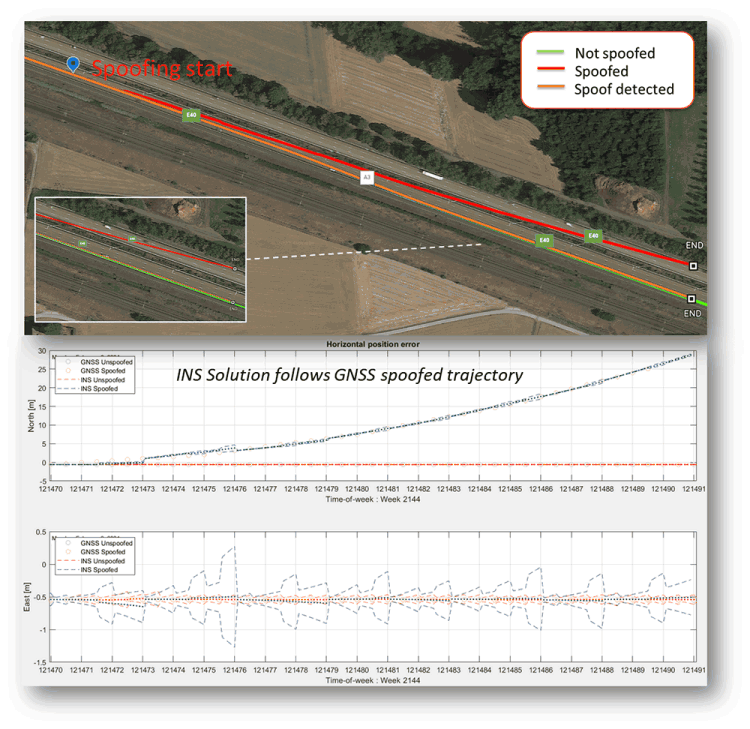
Figure 1 shows RAIM+ in action during a jamming and spoofing attack on a Septentrio GNSS receiver. While AIM+ removes the effects of GNSS jamming, both AIM+ and RAIM+ work together to block the spoofing attack.
| Tel: | +27 11 608 0144 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.nuvisionelec.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about NuVision Electronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved