NIST finds wireless performance consistent across 5G mmWave bands
29 June 2022
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
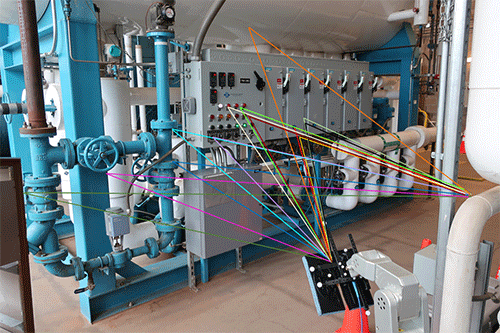
Wireless transmissions can take many routes to the intended receiver. The coloured lines are reconstructions of measured paths of millimetre-wave signals between a transmitter (not visible) and receiver (lower middle) in an NIST industrial control room. Each path is precisely characterised in terms of length and angle to the receiver. These paths are all secondary, meaning reflected or diffracted signals.
Settling a key dispute in the wireless communications field, researchers at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) found that transmission performance is consistent across different bands of the millimetre-wave (mmWave) spectrum targeted for high-speed, data-rich 5G systems.
Wireless systems are moving to the mmWave spectrum at 10-100 GHz, above crowded cellular frequencies as well as early 5G systems around 3 GHz. System operators tend to prefer lower bands of the new mmWave spectrum. One reason is that they are influenced by a formula that says more signals are lost at higher frequencies due to smaller wavelengths, resulting in a smaller useful antenna area. But until now, measurements of this effect by many organisations have disagreed over whether this is true.
NIST researchers developed a new method to measure frequency effects, using the 26,5-40 GHz band as a target example. After extensive study in the laboratory and two real-world environments, NIST results confirmed that the main signal path – over a clear “line of sight” between transmitter and receiver – does not vary by frequency, a generally accepted thesis for traditional wireless systems but until now not proven for the mmWave spectrum. The results are described in a new paper https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9759479.
The team also found that signal losses in secondary paths – where transmissions are reflected, bent or diffused into clusters of reflections – can vary somewhat by frequency, depending on the type of path. Reflective paths, which are the second strongest, and critical for maintaining connectivity, lost only a little signal strength at higher frequencies. The weaker bent and diffuse paths lost a bit more. Until now, the effects of frequency on this so-called multipath were unknown.
“This work may serve to demystify many misconceptions about propagation around higher frequencies in 5G and 6G,” NIST electrical engineer Camillo Gentile said. “In short, while performance will be worse at higher frequencies, the drop in performance is incremental, so we do expect the deployment at 5G and eventually at 6G to be successful.”
The NIST method emphasises innovative measurement procedures and enhanced equipment calibration to make sure only the transmission channel is measured. The researchers used NIST’s SAMURAI (Synthetic Aperture Measurement UnceRtainty for Angle of Incidence) channel sounder, which supports design and repeatable testing of 5G mmWave devices with unprecedented accuracy across a wide range of signal frequencies and scenarios. The NIST system is unique in that antenna beams can be steered in any direction for precise angle-of-arrival estimates.
NIST’s main innovations in the new study, as discussed in the paper, were calibration procedures to remove the effects of channel sounder equipment from the measurements, extension of an existing algorithm to determine from a single measurement how individual paths vary by frequency, and studies in an industrial control centre and a conference room to classify the types of paths involved and determine any frequency effects.
Further reading:
Module combines 5G and NTN support
Quectel Wireless Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Quectel Wireless Solutions announced the launch of its BG770A-SN ultra-compact 5G-ready satellite communication module, compliant with 3GPP releases 13, 14 and 17.
Read more...
Scalable and secure IoT device onboarding and management
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
EasyPass is an enhancement within Cambium’s cnMaestro platform, aimed at providing local businesses with secure, efficient, and scalable device management, making it ideal for high-demand environments such as educational institutions, retail spaces, and corporate campuses.
Read more...
SIMCom’s A7673X series
Otto Wireless Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
SIMCom’s A7673X series is a Cat 1 bis module that supports LTE-FDD, with a maximum downlink rate of 10 Mbps and an uplink rate of 5 Mbps.
Read more...
Non-terrestrial network module
Altron Arrow
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Fibocom unveiled its MA510-GL (NTN), a non-terrestrial networks module which is compliant with 3GPP Release 17 standard.
Read more...
Cellular IoT connectivity via satellite
Altron Arrow
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The Telit Cinterion cellular LPWA module will enable satellite data communication using the NB-IoT protocol, without any special hardware changes required for the integration of the cellular module in the customer application.
Read more...
Wireless module supports up to 600 Mbps
iCorp Technologies
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Quectel’s FCU865R is a high-performance Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.3 LCC package module which can be used for WLAN and Bluetooth connections.
Read more...
Unlocking the future of connectivity
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The battle for the 6 GHz spectrum band is heating up in South Africa, mirroring global debates on the allocation of spectrum between Wi-Fi and cellular operators.
Read more...
Quectel wireless module wins accolade
iCorp Technologies
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
The winners of the 2024 IoT Evolution 5G Leadership Award were recently announced, with Quectel walking away with an award for its modules which make 5G features more easily accessible for IoT applications, notably the company’s RG255C-GL.
Read more...
Innovative upgrade process for 2G/3G
Otto Wireless Solutions
Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
What is likely to happen during the sunset period for 2G and 3G signals, especially on the back of already near-obsolescence of 2G network equipment, is for the availability of the connectivity mediums to begin to reduce between now and the shutdown date.
Read more...
RFID in aviation: the ultimate solution to baggage mishandling
Osiris Technical Systems
Editor's Choice Telecoms, Datacoms, Wireless, IoT
Creating a solution that enables real-time tracking of airline baggage on a global scale seems like an impossible task when considering the number of airlines, airports, and passengers that flow through and between them.
Read more...

