Solution for synchronising multiple direct digital synthesizers
22 May 2002
DSP, Micros & Memory
The fast frequency hopping, extreme tuning resolution, and programmable phase control attributes of direct digital synthesizers (DDSs) make them a compelling choice for a wide variety of signal synthesis applications. However, many applications, such as phased-array radar and critical timing generators, require precise phase-synchronisation of multiple synthesized output signals. Phase synchronisation of multiple synthesizers is a challenge for PLL and other traditional analog-based architectures.
The AD9852/9854 and AD9850/9851 DDS devices from Analog Devices, with up to 14 bits of programmable phase-offset resolution (for AD9852/9854), provide an easy and precise solution for phase synchronisation of multiple synthesized signals. The synchronisation of multiple DDS devices is accomplished as follows.
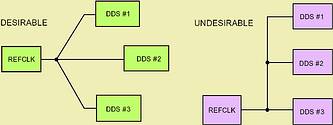
There are two basic timing requirements to be met in order for successful synchronisation to occur. The first, and somewhat obvious, is a coincidental REF clock between all DDSs. Coincidental means that the REF clock pins of each DDS have REF clock timing coincident in time (Figure 1). This is accomplished through proper PCB layout.
Figure 1. PCB layout must ensure that REFCLK edge arrives coincidentally at clock input pins of multiple DDSs
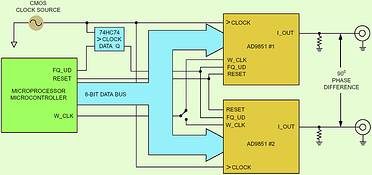
The second timing requirement between all DDS devices is the coincidental transfer of the programmed input data to the DDS core. Performing this transfer are two key signals: FQ_UD for the AD9850/9851 and I/O update clock for the AD9854/9852. If the rising edges of these two signals are sent synchronously to the multiple DDSs, along with proper set-up time relative to the REF clock, then synchronisation will be achieved (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Dual AD9851 set-up for quadrature output
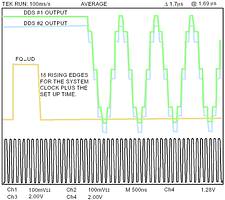
With proper procedure, synchronisation can be readily achieved among multiple DDSs; Figure 3 illustrates synchronisation of two AD9851 devices. In this case, the REFCLK frequency is set to 10 MSa/s. Synchronisation is also achievable up to the maximum system clock rate (including PLL mode).
Figure 3. DDS synchronisation (conditions: VCC = 5 V, REFCLK = 10 MSP, nonPLL mode, 25°C)
Typical applications are for clock synthesis, ADC encode generators, and agile local oscillators.
Further reading:
QuecPython live demonstration
Quectel Wireless Solutions
DSP, Micros & Memory
QuecPython allows designers to adapt Quectel’s modules quickly, with a low-code approach to suit their precise requirements in less time and at reduced cost, while maintaining high security standards.
Read more...
Robust and customisable SBC
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
Pairing the powerful i.MX8M Plus System on Module (SoM) from SolidRun, which features the i.MX 8M Plus SoC from NXP, this high-performance SBC is set to transform industrial environments.
Read more...
New family supports future cryptography
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
NXP has introduced its new i.MX 94 family, which contains an i.MX MPU with an integrated time-sensitive networking (TSN) switch, enabling configurable, secure communications with rich protocol support in industrial and automotive environments.
Read more...
Fast and reliable 4G connectivity worldwide
TRX Electronics
DSP, Micros & Memory
Powered by a powerful Quectel LTE Cat 4 modem, the Arduino Pro 4G module’s fast data throughput and high bandwidths ensure reliable and quick data download and upload, even in remote locations.
Read more...
NXP’s all-purpose microcontroller series
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
NXP has released its MCX A14x and A15x series of all-purpose microcontrollers which are part of the larger MCX portfolio that shares a common Arm Cortex-M33 core platform.
Read more...
ESP32-P4 SoC
iCorp Technologies
DSP, Micros & Memory
Espressif Systems announced its latest SoC, the ESP32-P4 which is powered by a RISC-V CPU, with an AI instructions extension, an advanced memory subsystem, and integrated high-speed peripherals.
Read more...
Microchip SoC FPGA
ASIC Design Services
DSP, Micros & Memory
Microchip Technology introduced the RT PolarFire SoC FPGA, the first real-time Linux capable, RISC-V-based microprocessor subsystem on a proven RT PolarFire FPGA platform.
Read more...
QLC Flash memory using BiCS tech
EBV Electrolink
DSP, Micros & Memory
KIOXIA announced it had started shipping its 2 Tb Quad-Level-Cell memory devices with its 8th-generation BiCS FLASH 3D flash memory technology.
Read more...
Low noise 3-axis MEMS accelerometers
Altron Arrow
DSP, Micros & Memory
The ADXL357 and ADXL357B from Analog Devices are digital outputs, low noise density, low 0 g offset drift, low power, three-axis accelerometers with selectable measurement ranges.
Read more...
ST’s biosensing tech enables next-gen wearables
Future Electronics
DSP, Micros & Memory
The highly integrated biosensor device combines an input channel for cardio and neurological sensing, with motion tracking and embedded AI core, for healthcare and fitness applications.
Read more...