
Fractional turn transformers are not a new idea but it is not a concept that appears to have been applied to AC/DC power supplies in the past. For multiple-output power supplies, in particular, it offers some significant advantages in terms of saving space, cutting cost and improving efficiency.
The challenge comes when multiple outputs are required. In a power supply where 5 V and 12 V outputs are needed, it would be ideal to have the 5 V winding as a single turn on the transformer, but the 12 V winding then becomes 2,5 turns, which cannot be manufactured. One solution is to make the 5 V winding two turns, then 5 turns are needed for the 12 V winding. But the low-voltage, high-current 5 V winding has to carry the full rated load of that output, so it is made from thick copper foil, and the transformer has to become much larger if the number of turns is doubled.
In another common scenario, 5 V and 3,3 V outputs might be required. Normally, a regulator is used on the 5 V output to produce the 3,3 V rail. This lowers efficiency, eats up board space and adds costs.
In both cases, what is known as a fractional turn transformer solves a lot of problems. The term ‘fractional turn’ can be a little misleading because it is not a device with partial turns or tapped turns, both of which would unbalance the transformer, even if they could be implemented. Rather, it is a small transformer with a number of windings that connect to the secondary of the power transformer. The arrangement of these windings, shown in Figure 1, can be used to effectively add or subtract to the output voltage from the power transformer’s secondary, depending on the phase in which it is connected. For example, where 5 V and 3,3 V are needed, the power transformer can be designed so that a single turn secondary winding delivers 4,5 V.
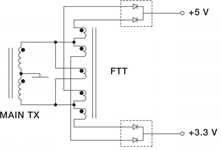
The separate fractional turns transformer adds 0,5 V to deliver a 5 V output and subtracts 1,2 V to produce the 3,3 V output. This additional transformer can be very small because it handles very little low power due to the low voltage present across each winding.
Where a 12 V output it needed, the same power transformer can use a 3-turn secondary to produce 13,5 V at its output, with a small fractional turn transformer utilised to reduce this to 12 V. Of course, the magic is in how the fractional turn transformer is designed and connected, but the general principle is very well demonstrated in XP Power’s RCL175 family of compact, multi-output 175 W AC/DC switchers, an example of which is shown in Figure 2.

Here, customers can specify any voltage within the operating range of each output and the company delivers what is effectively a custom power supply simply by modifying the transformer arrangement. The power supplies have industrial, IT and medical approvals.
For more information contact Edwin Brown, Vepac Electronics, +27 (0)11 453 1910, [email protected], www.arrow.altech.co.za
| Tel: | +27 11 454 8053 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.vepac.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Vepac Electronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved