
Android is an open source platform built by Google that includes an operating system, middleware and applications for the development of devices employing wireless communications. This article takes a look at the design of Android, how it works, and how it may be deployed to accelerate the development of a connected device.
Along with basic guidelines to getting started with Android, the Android SDK, its available tools and resources are reviewed and some consideration is given to applications for Android beyond conventional mobile handsets such as medical devices, consumer electronics and military/aerospace systems.
What is Android?
It is easy to think of Android as being yet another operating system for high-end mobile phones. It is really a software platform, rather than just an OS, that has the potential to be utilised in a much wider range of devices. In practical terms, Android is an application framework on top of Linux, which facilitates its rapid deployment in many domains. A key to its likely success is licensing. Android is open source and a majority of the source is licensed under Apache2, allowing adopters to add additional proprietary value in the Android source without source distribution requirements. Another way to appreciate the significance of Android is to take a historical perspective.
In the early days of PCs, the operating system was DOS. This presented some interesting challenges to application developers, as DOS provided a minimal number of services. The result was that every application needed a complete framework to provide the full functionality that was required. For example, a word processing program would need to have a driver for every imaginable printer. This was a major headache for developers and a serious ongoing maintenance problem.
The solution came in the early 1990s with the release of Windows. Or, rather, the development of Windows 3.0. Although we think of Windows as being primarily a GUI, it really is much more than that. Nowadays, a word processor just talks to a logical printer. The manufacturer of the printer hardware simply needs to provide a Windows driver and everything works together properly. In some respects, a similar situation exists today when developers want to deploy Linux for embedded applications. Android is the enabler for a broad application developer base, a complete stack on top of the Linux kernel.
Android history
Although Android is quite new technology, it does have a history. It really began in 2005 when Google acquired Android, which started rumours that Google had interests in mobile telephony. The Android product was announced, along with the formation of the Open Handset Alliance in 2007. The following year saw the first Android phone launched and the declaration of Android code as being open source.
Even though Android was created for handsets, many developers began to see a great opportunity to develop other kinds of innovative devices on the Android platform. Significant optimisations and additions would be required, however, to optimise Android for other connected devices. Late in 2008, a company called Embedded Alley Solutions of California, took on the challenge of moving Android beyond phones. In July 2009, Mentor Graphics acquired Embedded Alley.
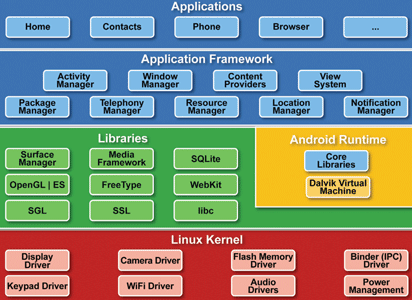
Android architecture
An Android system is a stack of software components. At the bottom of the stack is Linux – Linux 2.6 with approximately 115 patches. This provides basic system functionality like process and memory management and security. Also, the kernel handles all the things that Linux is really good at, such as networking and a vast array of device drivers, which take the pain out of interfacing to peripheral hardware. On top of Linux is a set of libraries including bionic (the Google libc), media support for audio and video, graphics and a lightweight database, which is a useful repository for storage and sharing of application data.
A key component of an Android system is the runtime – the Dalvik VM. This is not strictly a Java virtual machine. It was designed specifically for Android and is optimised in two key ways. It is designed to be instantiated multiple times – each application has its own private copy running in a Linux process. It is also designed to be very memory efficient, being register based (instead of being stack based like most Java VMs) and using its own bytecode implementation.
The Dalvik VM makes full use of Linux for memory management and multithreading, which is intrinsic in the Java language. It is important to appreciate that Android is not a Java virtual machine, but does use the Java language. The application framework provides many higher-level services to applications in the form of Java classes. This will vary in its facilities from one implementation to another.
A key Android capability is the sharing of functionality. Every application can export functionality for use by other applications in the system, thus promoting straightforward software re-use and a consistent user experience. At the top of the Android software stack are applications, a number of which are supplied as standard.
As mentioned, each application may also expose some of its functionality for use by others. For example, the message sending capability of the SMS application can be used by another application to send text messages. The supplied applications are not particularly ‘special’ – all Android applications have the same status in a given system. Although there are other options, Android applications are commonly implemented in Java utilising the Dalvik VM. Not only is the Dalvik highly efficient, but it also accommodates interoperability which results in application portability.
While all of these attributes are attractive, many developers will also want their C/C++ applications to run on an Android-based device.
Application development
Development environment
The standard Android development environment from Google is, as one might expect, Eclipse-based, using a plug-in to provide the necessary facilities. The developer needs to define their target configuration by specifying an Android Virtual Device. Code can then be executed on either the host-based emulator or a real device, which is normally connected via USB. This environment only supports Android development on ARM-based target devices. Recently, however, Mentor Graphics and others have ported Android to other processor architectures like MIPS.
Programming model
An Android application consists of a number of resources which are bundled into an archive – an Android package. Programs are generally written in Java, built using the standard Java tools, and then the output file is processed to generate specific code for the Dalvik VM. Each application runs in its own Linux process – an instantiation of the Dalvik VM – which protects its code and data from other applications. Of course, there are mechanisms for applications to transfer, exchange and share data.
An application is a set of components which are instantiated and run as required. There is not really an entry point or main() function. There are four types of application component: activities, services, broadcast receivers and content providers.
* An Activity is a functional unit of the application, which may be invoked by another activity. It has a user interface of some form. An application may incorporate a number of activities. One activity may be nominated as the default which means that it may be directly executed by the user.
* A Service is similar to an activity, except that it runs in the background without a UI. An example of a service might be a media player that plays music while the user performs other tasks.
* Broadcast Receivers simply respond to broadcast messages from other applications or from the system. For example, it may be useful for the application to know when a picture has been taken. This is the kind of event that may result in a broadcast message.
* A Content Provider supplies data from one application to others on request. Such requests are handled by the methods of the ContentResolver class. The data may be stored in the file system, the database or somewhere else entirely.
When an Android application is developed, the developer needs to describe it to the system and this is achieved by means of a manifest file. This is an XML file called AndroidManifest.xml which is stored in the root folder of the application’s file system. This outline example of a manifest file includes the definition of a single activity called MyActivity:

When an Android application wishes to obtain some functionality from another application or from the system, it can issue an intent. This is an asynchronous message that is used to activate an activity, service or broadcast receiver. For an activity or service, the specific action and location of data is included. Although an intent may include the specific activity required, it can be more generalised and the request resolved by the system. This mechanism is governed by Intent Filters. These filters specify what kind of intents the activities and services of an application can handle. They are described in the manifest file, thus:

Android development
Until very recently, Android deployment has been focused on mobile handsets. This was Google’s target market and the available software IP and development tools are designed and configured with this in mind. The potential for Android is enormous in other market areas – anywhere that sophisticated software, including connectivity and a user interface, encapsulates the functionality of a device.
Consumer, telecom, automotive, medical, and home applications are all attractive candidates for the deployment of Android. However, there are challenges in moving away from mobile handsets. Having a cool solution is great, but it is not useful unless it solves a real world problem. The challenge with electronic devices going forward is connectivity and interoperability. Android is well placed to address these issues. The Mentor Graphics approach to enabling Android to reach a wider market is to bring three key attributes to bear on the issue: the supply of development tools, software IP and professional services. The goal is to take Android and create specific editions, tailored to various markets.
Mentor Graphics support for Android
In July 2009, Mentor Graphics announced the acquisition of Embedded Alley. This company, founded by specialists in open software, brings extensive expertise in embedded Linux and Android, which complements Mentor’s existing competency in hard real-time operating systems. Underpinning the Embedded Alley approach is a clear commitment to focus on the needs of the customer, enabling them to leverage open software to address their specific requirements.
As mentioned previously, Android has been successfully deployed in the mobile handset market. To expand into other markets, investment is required in order to port Android to other CPUs and provide drivers etc, for new peripheral devices. This is where Mentor Graphics comes in.
Android lends itself to some specific applications:
* Handheld media players are not too far removed from mobile handsets and are well suited to Android.
* Now that digital video is well established around the world and with Internet connectivity becoming common, Android offers a good mix of capabilities for such applications.
In cars and other road vehicles, Android seems logical for infotainment devices such as satellite navigation. But it could also find a place in smart instrumentation.
* Medical devices are demanding applications, where ease of use and connectivity are key requirements. Again Android can score here.
* Around the home, new electronic devices are appearing regularly and, again, connectivity and a good user interface are top priorities.
* The computing power used in industrial applications is increasing all the time. Operator safety is critical, which demands an intuitive user interface. And, once again, connectivity is essential.
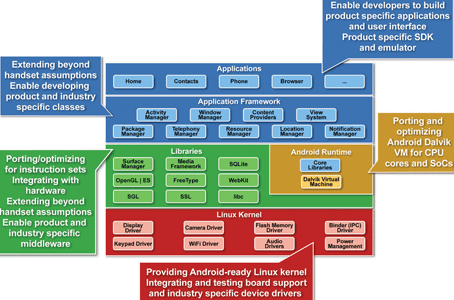
With reference to the Android system diagram in Figure 2, the requirements for specific attention can be identified:
* It is necessary to prepare Linux for a particular target. It also needs to be made Android-ready, which necessitates the careful application of numerous patches. Industry-specific drivers are also a likely requirement.
* The Dalvik VM needs to be ported to new CPUs and SoCs. It must be carefully tuned, as it is critical to application performance.
* The libraries need to be ported and optimised. Also, additional components will be needed for specific industries. Likewise the application framework.
* And last, developers need to be supported with writing new applications in Java for Android, and to allow new or existing C/C++ applications to run on their new Android-based device.
The development system for Android-based devices from Mentor Graphics is designed to address these goals. It includes the latest runtime and libraries optimised for specific CPUs. There is support for the development of custom board ports and drivers, along with customisation of the application framework and the emulator. The development system is Eclipse based and it is a core philosophy to align with a customer’s working practices, not to change them unnecessarily. The goal is to create reproducible, high quality code to deploy Android into multiple application domains.
Additional support is available in the form of professional services, leveraging Mentor’s Android expertise and experience to enable customers to get to market faster. When required, Mentor can support device developers throughout their entire product life cycle, from product requirements all the way through deployment, with complete Android services, including:
* Custom board ports.
* Extending I/O support.
* Integration of product- or industry-specific middleware.
* Application development.
* Functional, stress and performance testing, and benchmarking.
* Integration and support services.
Conclusion
Android is a disruptive technology, which was introduced initially on mobile handsets, but has much wider potential. There are challenges in the application of Android to other types of device. With its development system for Android-based devices and a full range of professional services, Mentor Graphics is well suited to support developers using Android and Linux for a wide range of embedded applications.
| Tel: | +27 11 315 8316 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.asic.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about ASIC Design Services |
© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved