
In August 2005, Trolley Scan developed a technology which allows an RFID system to not only identity the transponders, but also measure the distance of the transponder from the reader.
What is unique about this technology is that it has the ability to measure the distance travelled by the radio signal very accurately. In fact, as this article will show, accuracy of the system is better than one part in 40 000. The system can also measure the location of multiple transponders simultaneously and uses the same low cost passive and battery assisted transponders used in normal RFID readers.
The system uses the wavelength of the operating frequency of the signal travelling from the transponder to the reader as its 'yardstick'. The wavelength is based on a physical property, namely the speed at which radio waves travel, a value that is very accurately known. In fact the standard definition of the metre unit of length kept by ISO (International Standards Organisation) is defined in terms of wavelengths and the speed of light.
RFID-radar is a form of relatively low-cost RFID reader system and is commercially available. By attaching transponders to items, the RFID-radar is able to read the identity and positions of the transponders, effectively combining RFID and realtime locating systems (RTLS) in one device.
The system uses different types of transponders depending on required operating range.
Low cost passive transponders are used for short ranges (up to 13 metres) and long range battery assisted tags for ranges up to 40 metres.
The system currently has two levels of accuracy, namely 'absolute accuracy' which is currently about 0,5 metres, and 'relative accuracy' where the accuracy is approximately 1 millimetre. This article focuses on relative accuracy. In this mode, the system measures the changes in distance between the reader and the transponder very accurately.
Relative mode
Use of the system in relative mode allows small movements to be measured at long distances. Such uses might be to monitor movement of a bridge with traffic flow or temperature variation, the bulging of storage tanks with variations in storage content, bulging of a dam wall, slippage of a structure on a mountain with rainfall, movement of a structure in wind and similar situations.
A series of transponders would be attached to the structure, and the RFID-radar set up at a monitoring point some distance away. The radar would continually measure the distance from all of the transponders to the radar, reporting all the measurements once per second and giving approximately millimetre accuracy 24 hours per day.
Testing
To investigate the long term accuracy, a test was conducted using 24 500 measurements from seven transponders at different distances. The test collected all the data measured over one hour with each transponder being measured once per second. Different types of transponders were used, from passive credit card-sized types to battery assisted types. Table 1 shows the range of each transponder and its type, and the charts show the scatter for each situation.
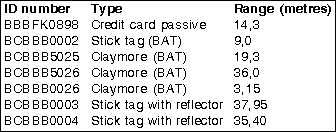
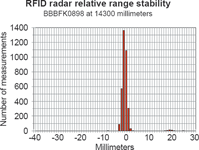
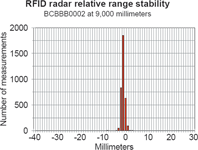

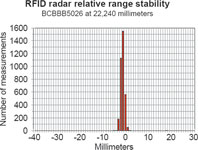
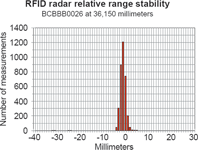


Conclusion
RFID-radar is an effective solution to a difficult problem, namely measuring small movements at long distances, using affordable solutions. Because the transponders are very cheap, it is commercially practical to mount this equipment in permanent monitoring situations to collect data on a 24 hour basis and generate alarms should variations be out of tolerance.
For more information contact Mike Marsh, Trolley Scan, +27 (0)11 648 2087.
| Tel: | +27 10 237 0675 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.trolleyscan.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Trolley Scan |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved