
In principle, the use of air/water heat exchangers for the cooling of electronic equipment and installations is not new. With the project of the IEC Committee SC 48 D however, structural parameters of standardised cabinets and general configurations of heat exchangers are brought together.
The benefit of such a standard is represented by the expected market development for standard products and their possible advance planning of performance parameters. Easy availability combined with cost savings through pre-manufactured components are further advantages of standard solutions.
The new standard
The new IEC/TS 62454 Ed.1.0 standard was published at the beginning of 2007. It relates to cabinets whose dimensions have been defined in the well-known standards IEC 60297 (19") and IEC 60917 (metric). The standard divides the water cooling of enclosures into three levels.
* Level I - Cabinet level.
* Level II - Shelf (subrack) level.
* Level III - Board level.
Level I
This level describes the framework conditions and supplies calculation examples for applications with air/water heat exchangers, which are either assembled at the base or the side of the cabinet. Independently of which solution is selected (base or side assembly), the user can now establish the required footprint for his application with the aid of selection curves or by calculation.
Level II
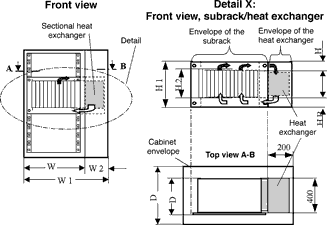
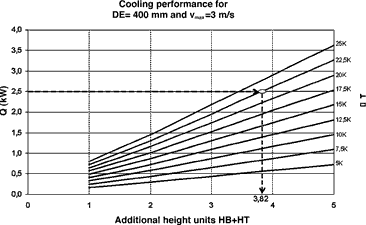
This level describes the framework conditions and supplies calculation examples for applications with small air/water heat exchangers, assembled at the side of the cabinet, which are only cooling parts of the cabinet, such as individual subracks or groups of subracks (Figure 1). The air/water heat exchangers planned for this solution by manufacturers and users - and now being defined by the standard -work with vertical air flow. This means that above and below the subrack/subracks an area for air circulation and redirection has to be allowed. How many U (rack units) the user has to calculate for this can be worked out with selection curves such as those shown in Figure 2, or with the aid of formulae.
Level III
This level deals with water cooling of individual components/chips directly on the boards. The possible cooling solutions are manifold, due to the many different dimensions and positions of the components that need to be cooled, so that the standard does not restrict this by tight definitions. Therefore, Level III only stipulates that there have to be water connections in the cabinet, leading to quick release connectors at the front or rear of the subracks (see Figure 3). Only the principle of water cooling of individual components is outlined. The detailed configuration is left to manufacturers and users.

Schroff supports Level I with a standard solution, whereby the heat exchanger is assembled laterally inside the cabinet. Thermodynamically, this will achieve the best possible level of effectiveness for a cabinet fully assembled with electronic plug-in units. For Level II and Level III, modular solutions are available which are configured to specific properties of the equipment or subracks. In these scenarios the standard defines the most important performance parameters.
| Tel: | +27 11 608 3001 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.actum.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Actum |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved