
Integration Associates' EZMac is a media access control module developed in C code, for use with Integration's ISM transceiver products and third-party MCUs to create very low cost mesh networks.
EZMac provides transceiver application designers with a simplified interface to the physical radio layer that manages the delivery of signals and their associated packets from the transmitter to the receiver, between nodes. Running in the background on the main CPU in two interrupt service routines, EZMac transmits data in short packets (16 byte maximum payload), and supports data transmission using the internal baud rate generator of the transceiver chip. The EZMac's state machine behaviour is determined by a set of parameters stored in the different registers.
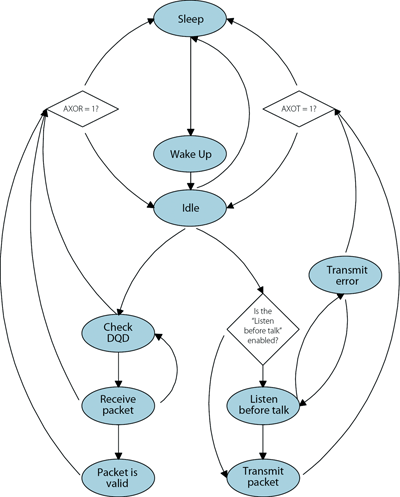
The MAC engine supports four basic modes (sleep, idle, transmit, and receive) via nine basic machine states (sleep, wake-up, idle, check DQD, receive packet, packet is valid, listen before talk, transmit packet, transmit error).
In addition to enabling the data communication automatically, EZMac provides a number of value-added features to ease application design while keeping the implementation to a simple, turnkey level. EZMac offers a range of addressing modes for customisable packet filtering, including customer ID, sender ID, destination ID, and packet length (see later for more details on packet filtering options). EZMac also works in connection with the receiver's DQD (data quality detector) to support fast frequency hopping when needed to find a valid packet transmission. Along with customisable addressing/filtering modes, EZMac provides comprehensive error detection and management capability, including collision error, synchronisation error, start of packet missing, bad CID, bad address, bad CRC, and bad packet length.
With the EZMac introduction, Integration has extended and deepened its EZRadio technology to include a configurable, embedded software layer to manage data packet delivery for its growing family of ISM transceiver products. With EZMac, the user simply defines the desired frequency band, and EZMac automatically initialises the transceiver with the optimal settings.
In addition to EZMac's nine basic machine states and their respective command functions, it provides a configurable packet filtering method to achieve the best fit with the application layer, as well as a comprehensive error detection method. EZMac also includes advanced feature commands for applications requiring even higher levels of control and customisation, where needed.
EZMac data communication packet configuration
EZMac transmits data in short packets, with a maximum payload of 16 bytes. It can be used in either peer-to-peer or master-slave communication networks with up to 255 addressable nodes (Figure 1). The synchronisation pattern is fixed (2DD4 hexadecimal).
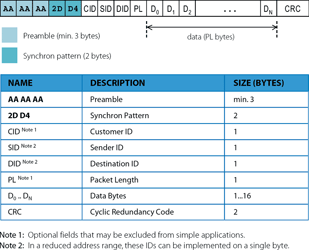
The optional customer ID (CID) byte is used to avoid unintended interactions between different systems using EZMac that may be installed in close proximity to one another. Sender ID (SID) and destination ID (DID) are used to uniquely identify the devices involved in the data communication. Packet length (PL) is used in applications where the number of transmitted data bytes needs to change dynamically. Cyclic redundancy code (CRC) is used to recognise if there is a bad data bit in the packet. Packet filtering runs in realtime, during reception, enabling EZMac to ignore invalid packets at a very early stage of the process. Realtime packet filtering save resources (processor power and battery life) and can significantly improve performance under some conditions by minimising the resources used on invalid packet processing.
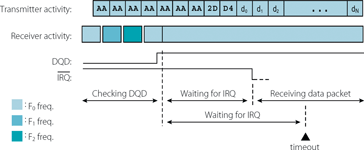
EZMac fast frequency hopping
The receiver's DQD signal is used to confirm an appropriate FSK transmission. After the first data byte has been received (do in Figure 2) the receiver sends an IRQ. If it does not do so within a given time, EZMac will change the receiver frequency to the next channel, and resume the search for a valid transmission. Fast frequency hopping is supported by means of a 1,75 ms listening and 250 μs frequency-hopping time (@9600 bps data rate, 4 MHz CPU clock, software SPI interface).
The EZMac state machine
EZMac is implemented as a state machine, running in two interrupt routines. The behaviour of EZMac is determined by a set of parameters stored in the different registers. The upper software layers can interact with EZMac via commands implemented in C. After initialisation, EZMac is in sleep mode, where the hardware is switched off. A minimum initialisation time of 5 ms is needed for the crystal oscillator to achieve stability. After waking up the transceiver with the wake up command, EZMac switches to idle mode. In this mode, all RF blocks are disabled to minimise current consumption while awaiting further commands. Before sending a transmit command, the data and destination are loaded into the appropriate registers. If the listen before talk feature is enabled, it will always check the channel before starting any packet transmission. If the check of the receiver DQD indicates that a valid FSK transmission is being performed, it will not interfere with the ongoing transmission. After transmission, it returns to idle mode (or sleep mode if enabled). If EZMac gets a receive command while in idle mode, it will change into receiving mode. It scans the available frequencies for a valid data transmission. Once a valid packet has been received, the transmission must then pass through all the enabled error detection and address filters. While the upper layers read out the data, EZMac returns to idle mode or sleep mode.
Licensing EZMac software
Developers of consumer or industrial product applications that employ embedded RF functionality, and that can use Integration's EZRadio products and EZMac software, may license EZMac in order to support the control of data between the developer's application, integration RFICs, and third party microcontrollers.
| Tel: | +27 11 608 0144 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.nuvisionelec.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about NuVision Electronics |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved