
USB interfaces are everywhere today, with low cost Flash memory drives and all kinds of USB peripherals being readily available, but these are very much focused on the PC market.
Attempt to make use of these peripherals in the 8 and 16 bit embedded market and one finds that implementation, cost and power consumption become major considerations. Part of this is down to the embedded controllers that are used in such systems. Devices such as the PIC family of controllers from Microchip are widely used with a broad range of memory densities and peripherals, but they lack the interfaces, resources and performance to incorporate a USB host controller.
In this example application, a VNC1L Vinculum controller IC provides the interface between the PIC as the system controller and a USB 2.0 full speed port. This allows, for example, a USB Flash memory drive connection to be accomplished with a minimum of implementation time and overhead.
Vinculum
The controller is based around a custom processor core with twin direct memory access (DMA) engines to accelerate data transfers and a 32-bit numeric co-processor to optimise the calculations for the file system - all in a single chip with 64 KB of embedded Flash program memory and 4 KB of internal data SRAM. Vinculum is specifically targeted at the embedded USB controller market and requires a minimum of external support components. One key feature of the Vinculum core is that its code length is significantly reduced compared with common MCU cores. Reducing the code overhead of the core allows much more functionality to be squeezed into the on-chip e-Flash memory. Such features are complementary to a PIC-based embedded system. The schematic of such a system is shown in the accompanying figure, using Vinculum to link a small PIC MCU to a USB 'A' connector and hence to a USB Flash drive.
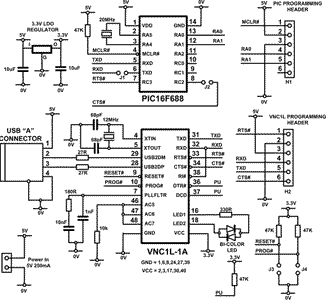
Schematic description
The PIC is the controller of the system, taking data from sensors or other sources via its general-purpose I/O pins (RC0, RC1, RA2 on pins 9,10,11), converting the data format and writing that data in a stream to a file on the Flash drive. Commands and data are sent via TXD (pin 6) to the VNC1L RXD (pin 32). VNC1L handles the FAT 12/16/32 file creation and data storage on the USB Flash drive, communicating with the drive via USB2DM and USB2DP on pins 28 and 29. Data is read from the Flash drive via the same pins, and sent from the VNC1L TXD (pin 31) to the RXD (pin 5) of the PIC for use by the system firmware.
The system is controlled by the firmware on the PIC, with the transfers controlled by instructions issued by the PIC and interpreted by the standard firmware on the Vinculum. Whilst that is a simple description of the system, there is more required to complete the design. The devices need power, crystals to control their clocks, and they need to be programmed.
Using a 20 MHz crystal on pins 2 and 3 of the PIC allows for higher baud rates of up to 115 200 bps in its UART interface, as opposed to the maximum 9600 bps achievable by using the internal 8 MHz oscillator, thus improving the performance of the system. PIC I/O pins RC2 and RC3 are used by the PIC firmware to simulate RTS/CTS handshake signals with the VNC1Ls UART interface.
A 5 V regulated power supply at 250 mA is required, providing up to 200 mA at the USB 'A' connector, 25 mA to power the VNC1L and 25 mA to power the PIC16F688. VNC1L requires a 3,3 V supply which is provided by a 3,3 V LDO regulator, and has 5 V-tolerant I/O pins which enable it to connect to the PIC without using level shifters.
For low power applications the VNC1L can be put into a 2 mA sleep mode when not required. To wake the device, the ring indicator (RI) pin (pin 38) of the UART interface can be strobed. If this is connected to the RXD line, as here, it can be triggered by an incoming dummy command to wake up the device.
This design also includes a bi-colour status LED indicator powered from pins 16 and 18. This indicates successful enumeration of the USB Flash drive and access to the file system.
VNC1L firmware
The VNC1L is programmed with standard firmware, called VDAP (Vinculum disk and peripheral) that interprets the commands coming from the PIC. These VDAP commands are DOS-like instructions such as DIR, RD and WR. The command set also supports single byte hex commands which are more suited to control by a microprocessor.
VDAP commands are included in the PIC firmware to control access to the USB Flash drive. A typical sequence would be to create a file, read/write data to the file and then close the file.
VNC1L and PIC programming
This design contains two programming headers, one for each device assuming that a development environment is desired. For a production design, both devices could be pre-programmed prior to insertion on a PCB, thus eliminating the headers and jumpers.
During normal operation, J1 and J2 should be populated and the other jumpers left open. To program the VNC1L, remove J1 and J2 jumpers to isolate the VNC1L UART inputs from the PIC outputs. Disconnect the 5 V power supply and then connect a TTL-232R-3V3 cable to H2. Connect the USB side of this cable to a PC with the VPROG programming utility installed. Populate J4 to pull the PROG# pin of the VNC1L low and temporarily short J3 to reset the device and put it into programming mode. After programming, remember to restore the jumper settings to the operational positions.
The programming header for the PIC connects to pins RA0 and RA1 and MCLR# of the device, with the 5 V programming voltage/supply being supplied via the header. Disconnect the 5 V power supply prior to programming the PIC microcontroller. The header would be connected to a standard PIC development environment such as a PICKit2, allowing Microchip's debug and downloading tools to be used.
In the sample C code provided by FTDI, the PIC waits for a Flash disk to be detected and then opens a file called hello.txt. The text 'Hello World' total with a carriage return and line feed characters are then written to the file. It then closes the file and waits for the disk to be removed.
Conclusion
FTDI's Vinculum VNC1L provides an easy to use, easy to program interface between a low cost microcontroller and a USB 2.0 low/full speed peripheral. The DOS-like command set allows a data transfer routine to be written and debugged easily within the microcontroller environment, and the simple layout provides a low cost USB Host implementation for embedded systems. This allows low cost, ubiquitous USB Flash drives as the data storage media for the system, as well as being able to provide software upgrades in the field. Though outside the scope of this article, the VNC1L device can also be used to connect many other USB peripherals besides mass storage devices.
The Vinculum IC also adds less than 10% of the power budget of the USB interface and even less to the power budget of the system, allowing for USB 2.0 Host Controller ports to be added to portable devices in a straightforward manner.
| Tel: | +27 11 728 4757 |
| Email: | info@mbsiliconsystems.co.za |
| www: | www.mbsiliconsystems.co.za |
| Articles: | More information and articles about MB Silicon Systems |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved